-
DBMS Tutorial
- dbms-tutorial
- what-is-database
- types-of-databases
- what-is-rdbms
- dbms-vs-rdbms
- dbms-vs-file-system
- dbms-architecture
- three-schema-architecture
- data-models
- data-model-schema
- data-independence
- dbms-language
- acid-properties-in-dbms
Data modeling
- er-model-concept
- notation-for-er-diagram
- er-design-issues
- mapping-constraints
- dbms-keys
- dbms-generalization
- dbms-specialization
- dbms-aggregation
- convert-er-into-table
- relationship-of-higher-degree
Relational data Model
- relational-model-concept
- relational-algebra
- join-operation
- integrity-constraints
- relational-calculus
Normalization
- functional-dependency
- inference-rule
- dbms-normalization
- dbms-1nf
- dbms-2nf
- dbms-3nf
- dbms-bcnf
- dbms-4nf
- dbms-5nf
- relational-decomposition
- multivalued-dependency
- join-dependency
- inclusion-dependence
- canonical-cover
Transaction Processing
- transaction
- transaction-property
- states-of-transaction
- dbms-schedule
- testing-of-serializability
- conflict-schedule
- view-serializability
- recoverability-of-schedule
- failure-classification
- log-based-recovery
- dbms-checkpoint
- deadlock-in-dbms
Concurrency Control
- concurrency-control
- lock-based-protocol
- time-stamping-protocol
- validation-based-protocol
- thomas-write-rule
- multiple-granularity
- recovery-concurrent-transaction
File organization
- file-organization
- sequential-file-organization
- heap-file-organization
- hash-file-organization
- b+-file-organization
- dbms-isam
- cluster-file-organization
Indexing and B+ Tree
Hashing
RAID
Misc
- decomposition-algorithms
- storage-system-in-dbms
- data-dictionary-storage
- file-organization-storage
- selection-of-raid-levels
- bitmap-indexing
- buffer-replacement-strategies
- database-buffer
- estimating-query-cost
- query-processing-in-dbms
- evaluation-of-expressions
- external-sort-merge-algorithm
- hash-join-algorithm
- materialization-in-query-processing
- merge-join-algorithm
- nested-loop-join-algorithm
- selection-operation-in-query-processing
- double-pipelined-join-algorithm
- implementation-of-pipelining
- pipelining-in-query-processing
- advanced-query-optimization
- transforming-relational-expressions
- candidate-key
- closure-of-an-attribute
- questions-on-boyce-codd-normal-form
- questions-on-normalization
- questions-on-third-normal-form
- equivalence-of-functional-dependency
- referential-integrity-constraint
- questions-on-lossy-and-lossless-decomposition
- lossy-or-lossless-decomposition-(second-method)
- questions-to-identify-normal-form
- types-of-relationship-in-database-table
- candidate-key-in-dbms
- primary-key-in-dbms
- super-key-in-dbms
- alternate-key-in-dbms
- composite-key-in-dbms
- foreign-key-in-dbms
- surrogate-key-in-dbms
- unique-key-in-dbms
- purpose-of-normalization
- commit-vs-rollback-in-sql
- ddl-vs-dml
- denormalization-in-databases
- er-model-vs-relational-model
SQL Introduction
- sql-introduction
- characteristics-of-sql
- advantage-of-sql
- sql-datatype
- sql-command
- sql-operator
- sql-table
- sql-select-statement
- sql-insert-statement
- sql-update-statement
- sql-delete-statement
- sql-view
- sql-index
- sql-sub-queries
- sql-clauses
- sql-aggregate-function
- sql-join
- sql-set-operation
DBMS MCQ
Interview Questions
Query Processing in DBMSQuery Processing is the activity performed in extracting data from the database. In query processing, it takes various steps for fetching the data from the database. The steps involved are:
The query processing works in the following way: Parsing and TranslationAs query processing includes certain activities for data retrieval. Initially, the given user queries get translated in high-level database languages such as SQL. It gets translated into expressions that can be further used at the physical level of the file system. After this, the actual evaluation of the queries and a variety of query -optimizing transformations and takes place. Thus before processing a query, a computer system needs to translate the query into a human-readable and understandable language. Consequently, SQL or Structured Query Language is the best suitable choice for humans. But, it is not perfectly suitable for the internal representation of the query to the system. Relational algebra is well suited for the internal representation of a query. The translation process in query processing is similar to the parser of a query. When a user executes any query, for generating the internal form of the query, the parser in the system checks the syntax of the query, verifies the name of the relation in the database, the tuple, and finally the required attribute value. The parser creates a tree of the query, known as 'parse-tree.' Further, translate it into the form of relational algebra. With this, it evenly replaces all the use of the views when used in the query. Thus, we can understand the working of a query processing in the below-described diagram: 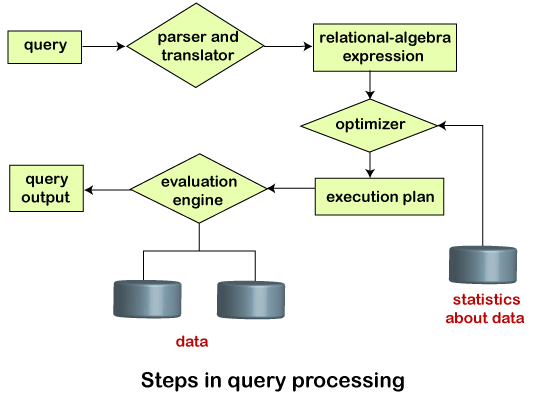 Suppose a user executes a query. As we have learned that there are various methods of extracting the data from the database. In SQL, a user wants to fetch the records of the employees whose salary is greater than or equal to 10000. For doing this, the following query is undertaken: select emp_name from Employee where salary>10000; Thus, to make the system understand the user query, it needs to be translated in the form of relational algebra. We can bring this query in the relational algebra form as:
After translating the given query, we can execute each relational algebra operation by using different algorithms. So, in this way, a query processing begins its working. EvaluationFor this, with addition to the relational algebra translation, it is required to annotate the translated relational algebra expression with the instructions used for specifying and evaluating each operation. Thus, after translating the user query, the system executes a query evaluation plan. Query Evaluation Plan
Optimization
Finally, after selecting an evaluation plan, the system evaluates the query and produces the output of the query. Next Topic#
|