-
Java Tutorial
- what-is-java
- history-of-java
- features-of-java
- c++-vs-java
- hello-java-program
- program-internal
- how-to-set-path?
- jdk,-jre-and-jvm
- jvm:-java-virtual-machine
- java-variables
- java-data-types
- unicode-system
- operators
- keywords
Control Statements
- java-if-else
- java-switch
- java-for-loop
- java-while-loop
- java-do-while-loop
- java-break
- java-continue
- java-comments
- java-programs
Java Object Class
- java-oops-concepts
- naming-convention
- object-and-class
- method
- constructor
- static-keyword
- this-keyword
Java Inheritance
Java Polymorphism
- method-overloading
- method-overriding
- covariant-return-type
- super-keyword
- instance-initializer-block
- final-keyword
- runtime-polymorphism
- dynamic-binding
- instanceof-operator
Java Abstraction
Java Encapsulation
Java Array
Java OOPs Misc
- object-class
- object-cloning
- math-class
- wrapper-class
- java-recursion
- call-by-value
- strictfp-keyword
- javadoc-tool
- command-line-arg
- object-vs-class
- overloading-vs-overriding
Java String
- what-is-string
- immutable-string
- string-comparison
- string-concatenation
- substring
- methods-of-string-class
- stringbuffer-class
- stringbuilder-class
- string-vs-stringbuffer
- stringbuffer-vs-builder
- creating-immutable-class
- tostring-method
- stringtokenizer-class
- java-string-faqs
Java String Methods
- string-charat()
- string-compareto()
- string-concat()
- string-contains()
- string-endswith()
- string-equals()
- equalsignorecase()
- string-format()
- string-getbytes()
- string-getchars()
- string-indexof()
- string-intern()
- string-isempty()
- string-join()
- string-lastindexof()
- string-length()
- string-replace()
- string-replaceall()
- string-split()
- string-startswith()
- string-substring()
- string-tochararray()
- string-tolowercase()
- string-touppercase()
- string-trim()
- string-valueof()
Java Regex
Exception Handling
- java-exceptions
- java-try-catch-block
- java-multiple-catch-block
- java-nested-try
- java-finally-block
- java-throw-keyword
- java-exception-propagation
- java-throws-keyword
- java-throw-vs-throws
- final-vs-finally-vs-finalize
- exception-handling-with-method-overriding
- java-custom-exceptions
Java Inner Class
- what-is-inner-class
- member-inner-class
- anonymous-inner-class
- local-inner-class
- static-nested-class
- nested-interface
Java Multithreading
- what-is-multithreading
- life-cycle-of-a-thread
- creating-thread
- thread-scheduler
- sleeping-a-thread
- start-a-thread-twice
- calling-run()-method
- joining-a-thread
- naming-a-thread
- thread-priority
- daemon-thread
- thread-pool
- thread-group
- shutdownhook
- performing-multiple-task
- garbage-collection
- runtime-class
Java Synchronization
- synchronization-in-java
- synchronized-block
- static-synchronization
- deadlock-in-java
- inter-thread-comm
- interrupting-thread
- reentrant-monitor
Java I/O
- java-input/output
- fileoutputstream
- fileinputstream
- bufferedoutputstream
- bufferedinputstream
- sequenceinputstream
- bytearrayoutputstream
- bytearrayinputstream
- dataoutputstream
- datainputstream
- java-filteroutputstream
- java-filterinputstream
- java-objectstream
- java-objectstreamfield
- console
- filepermission
- writer
- reader
- filewriter
- filereader
- bufferedwriter
- bufferedreader
- chararrayreader
- chararraywriter
- printstream
- printwriter
- outputstreamwriter
- inputstreamreader
- pushbackinputstream
- pushbackreader
- stringwriter
- stringreader
- pipedwriter
- pipedreader
- filterwriter
- filterreader
- file
- filedescriptor
- randomaccessfile
- java.util.scanner
Java Serialization
Java Networking
- networking-concepts
- socket-programming
- url-class
- urlconnection-class
- httpurlconnection
- inetaddress-class
- datagramsocket-class
Java AWT & Events
- awt-basics
- event-handling
- awt-button
- awt-label
- awt-textfield
- awt-textarea
- awt-checkbox
- awt-checkboxgroup
- awt-choice
- awt-list
- awt-canvas
- awt-scrollbar
- awt-menuitem-menu
- awt-popupmenu
- awt-panel
- awt-dialog
- awt-toolkit
- java-actionlistener
- java-mouselistener
- mousemotionlistener
- java-itemlistener
- java-keylistener
- java-windowlistener
- java-adapter-classes
- close-awt-window
Java Swing
- swing-introduction
- java-jbutton
- java-jlabel
- java-jtextfield
- java-jtextarea
- java-jpasswordfield
- java-jcheckbox
- java-jradiobutton
- java-jcombobox
- java-jtable
- java-jlist
- java-joptionpane
- java-jscrollbar
- java-jmenuitem-jmenu
- java-jpopupmenu
- java-jcheckboxmenuitem
- java-jseparator
- java-jprogressbar
- java-jtree
- java-jcolorchooser
- java-jtabbedpane
- java-jslider
- java-jspinner
- java-jdialog
- java-jpanel
- java-jfilechooser
- java-jtogglebutton
- java-jtoolbar
- java-jviewport
- java-jframe
- java-jcomponent
- java-jlayeredpane
- java-jdesktoppane
- java-jeditorpane
- java-jscrollpane
- java-jsplitpane
- java-jtextpane
- java-jrootpane
- using-tooltip
- change-title-icon
- executable-jar-file
- digital-watch
- graphics-in-swing
- displaying-image
Java Swing Apps
- notepad
- calculator
- ip-finder
- word-counter
- url-source-generator
- folder-explorer
- puzzle-game
- pic-puzzle-game
- tic-tac-toe-game
- online-exam
LayoutManagers
- borderlayout
- gridlayout
- flowlayout
- boxlayout
- cardlayout
- gridbaglayout
- grouplayout
- springlayout
- scrollpanelayout
JavaFX Tutorial
- javafx-tutorial
- install-java
- install-eclipse
- javafx-with-eclipse
- javafx-architecture
- application-structure
- first-javafx-application
JavaFX 2D Shapes
- javafx-2d-shapes
- shape-properties
- javafx-line
- javafx-rectangle
- javafx-ellipse
- javafx-arc
- javafx-circle
- javafx-polygons
- cubic-curve
- quad-curve
- javafx-color
- gradient-color
JavaFX Text
JavaFX Effects
- javafx-effects
- javafx-coloradjust
- javafx-colorinput
- javafx-imageinput
- javafx-blend
- javafx-bloom
- javafx-glow
- javafx-boxblur
- javafx-gaussianblur
- javafx-motionblur
- javafx-reflection
- javafx-sepiatone
- javafx-shadow
- javafx-dropshadow
- javafx-innershadow
- javafx-lighting
- javafx-light.distant
- javafx-light.spot
- javafx-light.point
JavaFX Transformation
- javafx-transformation
- javafx-translation
- javafx-rotation
- javafx-scaling
- javafx-shearing
- multiple-transformations
JavaFX Animation
- javafx-animation
- javafx-rotate-transition
- javafx-scale-transition
- javafx-translate-transition
- javafx-fade-transition
- javafx-fill-transition
- javafx-stroke-transition
- javafx-sequential-transition
- javafx-parallel-transition
- javafx-pause-transition
- javafx-path-transition
JavaFX 3D Shapes
JavaFX Layouts
- javafx-layouts
- javafx-borderpane
- javafx-hbox
- javafx-vbox
- javafx-stackpane
- javafx-gridpane
- javafx-flowpane
JavaFX UI
- javafx-ui-controls
- javafx-label
- javafx-button
- javafx-radiobutton
- javafx-checkbox
- javafx-textfield
- javafx-passwordfield
- javafx-hyperlink
- javafx-slider
- javafx-progressbar
- progress-indicator
- javafx-scrollbar
- javafx-filechooser
- javafx-menu
- javafx-tooltip
JavaFX Charts
- javafx-charts
- javafx-pie-chart
- javafx-line-chart
- javafx-area-chart
- javafx-bar-chart
- javafx-bubble-chart
- javafx-scatter-chart
- stacked-area-chart
- stacked-bar-chart
JavaFX CSS
Media with JavaFX
JavaFX Event Handling
Java Applet
- applet-basics
- graphics-in-applet
- displaying-image-in-applet
- animation-in-applet
- eventhandling-in-applet
- japplet-class
- painting-in-applet
- digital-clock-in-applet
- analog-clock-in-applet
- parameter-in-applet
- applet-communication
Java Reflection
- reflection-api
- newinstance()-method
- javap-tool
- creating-javap-tool
- creating-appletviewer
- call-private-method
Java 8 Date Time
- java-date-time-api
- java-localdate
- java-localtime
- java-localdatetime
- java-monthday
- java-offsettime
- java-offsetdatetime
- java-clock
- java-zoneddatetime
- java-zoneid
- java-zoneoffset
- java-year
- java-yearmonth
- java-period
- java-duration
- java-instant
- java-dayofweek-enum
- java-month-enum
Java Date (Classical)
Java Date Format
Current Date Time
Java Conversion
- java-string-to-int
- java-int-to-string
- java-string-to-long
- java-long-to-string
- java-string-to-float
- java-float-to-string
- java-string-to-double
- java-double-to-string
- java-string-to-date
- java-date-to-string
- java-string-to-char
- java-char-to-string
- java-string-to-object
- java-object-to-string
- java-int-to-long
- java-long-to-int
- java-int-to-double
- java-double-to-int
- java-char-to-int
- java-int-to-char
- java-string-to-boolean
- java-boolean-to-string
- date-to-timestamp
- timestamp-to-date
- binary-to-decimal
- decimal-to-binary
- hex-to-decimal
- decimal-to-hex
- octal-to-decimal
- decimal-to-octal
Java Collections
- collection-framework
- java-arraylist
- java-linkedlist
- arraylist-vs-linkedlist
- java-list-interface
- java-hashset
- java-linkedhashset
- java-treeset
- queue-priorityqueue
- deque-arraydeque
- java-map-interface
- java-hashmap
- working-of-hashmap
- java-linkedhashmap
- java-treemap
- java-hashtable
- hashmap-vs-hashtable
- java-enumset
- java-enummap
- collections-class
- sorting-collections
- comparable-interface
- comparator-interface
- comparable-vs-comparator
- properties-class
- arraylist-vs-vector
- java-vector
- java-stack
Java JDBC
- jdbc-introduction
- jdbc-driver
- db-connectivity-steps
- connectivity-with-oracle
- connectivity-with-mysql
- access-without-dsn
- drivermanager
- connection
- statement
- resultset
- preparedstatement
- resultsetmetadata
- databasemetadata
- store-image
- retrieve-image
- store-file
- retrieve-file
- callablestatement
- transaction-management
- batch-processing
- rowset-interface
- jdbc-mcq
Java New Features
Java 9 Features
- java-9-features
- interface-private-methods
- try-with-resources
- anonymous-classes
- safevarargs-annotation
- collection-factory-methods
- process-api-improvement
- version-string-scheme
- jshell-(repl)
- module-system
- control-panel
- stream-api-improvement
- underscore-keyword
Java 8 Features
- java-8-features
- lambda-expressions
- method-references
- functional-interfaces
- stream-api
- stream-filter
- base64-encode-decode
- default-methods
- foreach()-method
- collectors-class
- stringjoiner-class
- optional-class
- javascript-nashorn
- parallel-array-sort
- type-inference
- parameter-reflection
- type-annotations
- jdbc-improvements
Java 7 Features
- binary-literals
- switch-with-string
- java-7-multi-catch
- try-with-resources
- type-inference
- numeric-literals
- java-7-jdbc
Java 4/5 Features
- java-assertion
- java-for-each-loop
- java-varargs
- java-static-import
- java-autoboxing
- java-enums
- java-annotations
- java-generics
RMI
Internationalization
Java ArrayList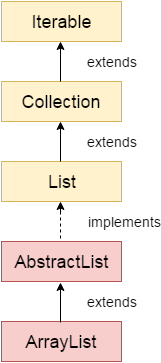 Java ArrayList class uses a dynamic array for storing the elements. It is like an array, but there is no size limit. We can add or remove elements anytime. So, it is much more flexible than the traditional array. It is found in the java.util package. It is like the Vector in C++. The ArrayList in Java can have the duplicate elements also. It implements the List interface so we can use all the methods of List interface here. The ArrayList maintains the insertion order internally. It inherits the AbstractList class and implements List interface. The important points about Java ArrayList class are:
Hierarchy of ArrayList classAs shown in the above diagram, Java ArrayList class extends AbstractList class which implements List interface. The List interface extends the Collection and Iterable interfaces in hierarchical order. ArrayList class declarationLet's see the declaration for java.util.ArrayList class. Constructors of ArrayList
Methods of ArrayList
Java Non-generic Vs. Generic CollectionJava collection framework was non-generic before JDK 1.5. Since 1.5, it is generic. Java new generic collection allows you to have only one type of object in a collection. Now it is type safe so typecasting is not required at runtime. Let's see the old non-generic example of creating java collection. Let's see the new generic example of creating java collection. In a generic collection, we specify the type in angular braces. Now ArrayList is forced to have the only specified type of objects in it. If you try to add another type of object, it gives compile time error. For more information on Java generics, click here Java Generics Tutorial. Java ArrayList ExampleOutput: [Mango, Apple, Banana, Grapes] Iterating ArrayList using IteratorLet's see an example to traverse ArrayList elements using the Iterator interface. Output: Mango Apple Banana Grapes Iterating ArrayList using For-each loopLet's see an example to traverse the ArrayList elements using the for-each loop Output: Test it NowMango Apple Banana Grapes Get and Set ArrayListThe get() method returns the element at the specified index, whereas the set() method changes the element. Output: Returning element: Apple Mango Dates Banana Grapes How to Sort ArrayListThe java.util package provides a utility class Collections which has the static method sort(). Using the Collections.sort() method, we can easily sort the ArrayList. Output: Apple Banana Grapes Mango Sorting numbers... 1 11 21 51 Ways to iterate the elements of the collection in JavaThere are various ways to traverse the collection elements:
Iterating Collection through remaining waysLet's see an example to traverse the ArrayList elements through other ways Output: Traversing list through List Iterator: Ajay Ravi Vijay Ravi Traversing list through for loop: Ravi Vijay Ravi Ajay Traversing list through forEach() method: Ravi Vijay Ravi Ajay Traversing list through forEachRemaining() method: Ravi Vijay Ravi Ajay User-defined class objects in Java ArrayListLet's see an example where we are storing Student class object in an array list. Output: 101 Sonoo 23
102 Ravi 21
103 Hanumat 25
Java ArrayList Serialization and Deserialization ExampleLet's see an example to serialize an ArrayList object and then deserialize it. Output: [Ravi, Vijay, Ajay] Java ArrayList example to add elementsHere, we see different ways to add an element. Output: Initial list of elements: [] After invoking add(E e) method: [Ravi, Vijay, Ajay] After invoking add(int index, E element) method: [Ravi, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay] After invoking addAll(Collection c) method: [Ravi, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay, Sonoo, Hanumat] After invoking addAll(int index, Collection c) method: [Ravi, John, Rahul, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay, Sonoo, Hanumat] Java ArrayList example to remove elementsHere, we see different ways to remove an element. Output: An initial list of elements: [Ravi, Vijay, Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav] After invoking remove(object) method: [Ravi, Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav] After invoking remove(index) method: [Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav] Updated list : [Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav, Ravi, Hanumat] After invoking removeAll() method: [Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav] After invoking removeIf() method: [Anuj, Gaurav] After invoking clear() method: [] Java ArrayList example of retainAll() methodOutput: iterating the elements after retaining the elements of al2
Ravi
Java ArrayList example of isEmpty() methodOutput: Is ArrayList Empty: true After Insertion Is ArrayList Empty: false Java ArrayList Example: BookLet's see an ArrayList example where we are adding books to list and printing all the books. Output: 101 Let us C Yashwant Kanetkar BPB 8 102 Data Communications and Networking Forouzan Mc Graw Hill 4 103 Operating System Galvin Wiley 6 Related TopicsDifference between Array and ArrayList When to use ArrayList and LinkedList in Java Difference between ArrayList and LinkedList Difference between ArrayList and Vector How to Compare Two ArrayList in Java How to reverse ArrayList in Java When to use ArrayList and LinkedList in Java How to make ArrayList Read Only Difference between length of array and size() of ArrayList in Java How to Synchronize ArrayList in Java How to convert ArrayList to Array and Array to ArrayList in java How to Sort Java ArrayList in Descending Order How to remove duplicates from ArrayList in Java Next TopicJava LinkedList
|